LEARN ABOUT OUR BREAST HEALTH PROGRAM
Clearer Imaging For Better Breast Cancer Detection
Also known as Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT), 3-D mammography is the latest breakthrough in breast cancer detection. For some women, images of cancers can often be obscured by dense breast tissue, causing some cancers to go undetected.
Benefits of 3-D Mammography include:
- 29% increase in detection of all breast cancers
- 41% increase in detection of invasive breast cancers
- Greater accuracy in pinpointing size, shape and location of tumors
- Fewer unnecessary biopsies or additional tests
- Greater likelihood of finding multiple tumors, which occurs in 15% of women with breast cancer
Why 3-D Breast Screening Is More Accurate
2-D mammography typically takes two X-rays of each breast from different angles—from side-to-side and top-to-bottom. The breast is stretched and compressed. This compression causes overlapping of the breast tissue, which can sometimes hide a breast cancer. Mammograms take a single picture across the entire breast.
Whereas 2-D mammography produces just a single picture of each breast, 3-D mammography takes multiple pictures of each breast from many angles. During the imaging session, an X-ray tube moves in an arc around the breast, taking a volume set of images in a matter of seconds. The breast radiology specialist then reviews the clear, highly focused images of the breast tissue, layer by layer.
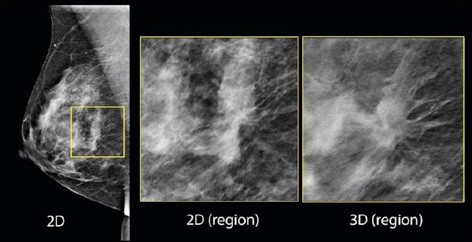
The images below show the difference between a 2-D and 3-D mammogram of the same region. The tumor is obvious on the 3-D view and could easily be missed on the 2-D view.
Quality You Can Trust
In addition to receiving some of the highest scores possible by the American College of Radiology (ACR), our Breast Imaging Centers in Walnut Creek and Concord have also been designated as Breast Imaging Centers of Excellence—the highest award given to breast imaging centers by ACR.
How To Schedule a 3-D Screening Mammogram
- All 3-D screening mammograms require a doctor's order. Need a doctor? Find a Doctor now.
- Once your doctor places your 3-D screening mammogram order, use MyChart to schedule online by logging in and selecting Visits > Schedule new appointment.
- You or your doctor can also schedule at any of our locations by calling our centralized scheduling phone number (925) 952-2701 or faxing orders to (925) 941-4065.
- Contact your health insurance carrier directly to find out if this service is covered by your health plan.
View Video
Awards

Our Breast Imaging Centers are recognized as Breast Imaging Centers of Excellence, the highest award given by the American College of Radiology (ACR).